Revolutionizing Radiology
We will delve into the latest developments in radiology and explore how they are shaping the future of medical imaging.
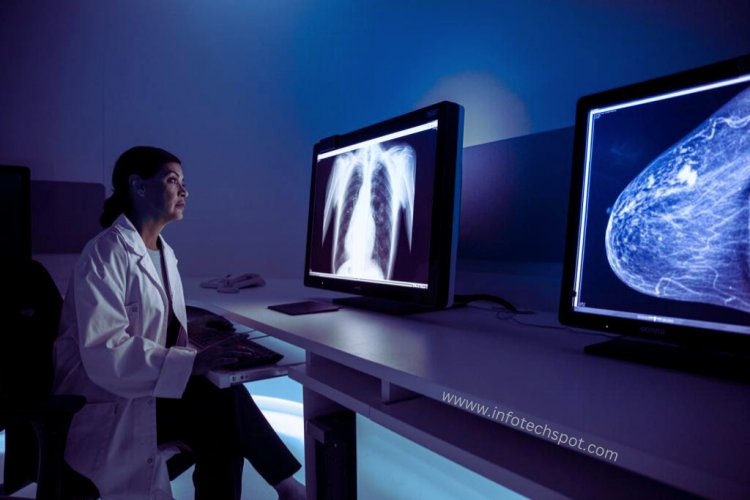
The Future of Medical Imaging
Radiology, a branch of medical science that employs various imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases, has come a long way since its inception. With advancements in technology and innovative approaches, it has revolutionized healthcare, enabling accurate diagnoses and effective treatment planning. In this article, we will delve into the latest developments in it and explore how they are shaping the future of medical imaging.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Radiology:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer in it, transforming the way medical images are analyzed and interpreted. AI algorithms, trained on massive datasets, can quickly and accurately detect abnormalities, assisting radiologists in making more precise diagnoses. These algorithms can also prioritize urgent cases, leading to faster turnaround times and improved patient care.
Moreover, AI-powered software can integrate patient data, such as electronic health records, to provide a comprehensive view of the patient's medical history, aiding radiologists in making more informed decisions. AI algorithms can also predict disease progression and treatment response, contributing to personalized medicine.
3D Printing in Radiology :
The advent of 3D printing has revolutionized radiology by enabling the creation of detailed physical models from medical imaging data. These models assist surgeons in planning complex procedures, such as organ transplants or tumor removals, by allowing them to visualize patient-specific anatomical structures before entering the operating room. This technology reduces the risk of complications and improves surgical outcomes.
Additionally, 3D-printed anatomical models serve as valuable educational tools for medical students and healthcare professionals, enhancing their understanding of complex anatomical structures and pathology. They also enable patient education, as physicians can use tangible models to explain diagnoses and treatment plans more effectively.
Advances in Imaging Modalities :
The field of radiology has witnessed significant advancements in imaging modalities, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and patient comfort. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanners now offer faster imaging times and higher resolution, enabling more detailed visualization of soft tissues and improved detection of abnormalities.
Computed Tomography (CT) scanners have also undergone remarkable improvements, with the development of low-dose techniques that reduce radiation exposure while maintaining image quality. Furthermore, dual-energy CT scanners provide valuable information about tissue composition, aiding in the differentiation of various pathologies.
Ultrasound technology has advanced with the integration of Artificial Intelligence, facilitating automated measurements and enhanced visualization. This has expanded its utility in various clinical scenarios, such as fetal imaging and musculoskeletal assessments.
The Role of Big Data and Cloud Computing :
The integration of big data and cloud computing has revolutionized it in multiple ways. The vast amounts of data generated by medical imaging studies can now be stored securely in the cloud, providing remote access to patient information for healthcare professionals worldwide. This enables efficient collaboration, second opinions, and telemedicine, particularly in underserved areas.
Big data analytics also contribute to research and quality improvement initiatives in it. By analyzing large datasets, researchers can identify patterns, develop predictive models, and improve imaging protocols, leading to enhanced diagnostic accuracy and optimized patient care.
Conclusion :
It continues to evolve at a rapid pace, thanks to advancements in technology and innovative approaches. Artificial intelligence has emerged as a powerful tool in it, aiding in accurate diagnoses, personalized medicine, and improved patient outcomes. 3D printing has revolutionized surgical planning and patient education, while advances in imaging modalities have enhanced diagnostic capabilities and patient comfort. The integration of big data and cloud computing has facilitated remote access, collaboration, and research in it. As we look to the future, it is evident that it will play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of healthcare, enabling early detection, precise treatment planning, and improved patient outcomes.













